Disaster-Preparedness
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Contents
Platforms
Motion Sensor
Under construction until the end of Fall 2014 semester unless indicated otherwise.
Purpose
- Detect and measure motion.
- Use multiple cheap, inexpensive sensors to increase accuracy/reliability/functionality.
- Be cheap and portable.
- Provide data that can be aggregated over a network.
Sensors
We used tilt switches, a piezo element, a laser / photoresistor combo, and an accelerometer.
Tilt
Use
- A tilt switch uses a material to complete a circuit (E.G. press a button) when it reaches either end of the container.
- We used XZ mercury switches.
- The Y direction wasn't very sensitive. It only seemed useful for seeing if the device had flipped over.
- Tilt switches work best when the motion is parallel to them. This loss of motion can be minimized by adding more sensors at half-steps. For example, we could add a tilt that was inbetween XZ to measure diagonal motion more effectively.
- We looked exclusively for change. This means we didn't care about what state the tilt switch was in, just if it had changed since the last read.
- No noticeable noise.
Wiring
- Power, ground, and signal.
- 10k resistor on power.
- Signal is digital.
Code Sample
const int tiltPin = 2;
int tiltState = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(tiltPin, INPUT);
}
void loop(){
tiltState = digitalRead(tiltPin);
}
Resources
Piezo Element
Use
- A very cheap, diverse piece of kit.
- Can be used as a button, a knock sensor, to detect vibration, to detect sound, or to produce sound similar to a buzzer.
- We used it as a vibration sensor.
- Vibration sensitivity is increased dramatically when the piezo element is attached to a solid object by a weight, glue, or tape.
Wiring
- Signal and ground. Signal serves as power.
- 1k resistor on the signal; 10k worked similarly, so 1k+ is probably fine
- analog
- minimal noise
Code Sample
const int piezoPin = 2;
int piezoState = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(piezoPin, INPUT);
}
void loop(){
piezoState = analogRead(piezoPin);
}
Resources
Housing
Case
Resonate Frequency
Power
Code
Research
These are notes and observations from research.
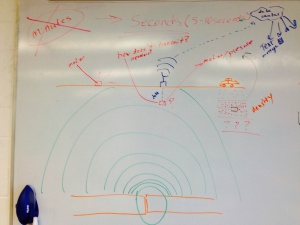
Earthquake
- occur due to movement in tectonic plates
- only seconds of notice, 5-10 seconds
- [p waves] are much faster than [s waves] and the actual waves that cause the earthquake.
- earthquakes travel at about the same speed as data networks
- can be measured by motion (on surface or underground) and pressure (underground)
- downside of underground monitoring is 1) power and 2) transmission
- can use repeaters or solar power to solve these issues
- advantage of being underground is distance from noise (such as animals and humans) and being closer to the source of the earthquake
- being attached to rock is good
- downside of underground monitoring is 1) power and 2) transmission
Resources
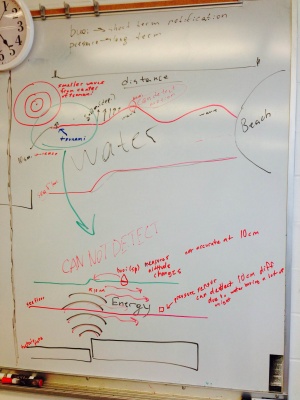
Tsunami
- in the deep sea pressure sensors are used to measure the relatively small sea-level change (in centimeters)
- nearer to shore, where waves start to form, altitude could be measured by buoy
- travel at hundreds of miles per hour
- tsunami headquarters in Hawaii
- notification could be minutes to hours in advance depending on distance from source of tsunami
- height/speed of wave reduces with distance