Difference between revisions of "Cs-history"
(→Hardware Resources) |
m (Fix link) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
All through the 1990s and 2000s we have continued to work with local Earlham Computer Science alums who teach as adjuncts periodically. Ray Ontko ('84) and Chris Hardie ('99) are the two we have worked with to-date and plan to continue engaging in the future. The organizations they run are also collectively responsible for the current employment of about 12 Earlham Computer Science graduates; and many more historically. | All through the 1990s and 2000s we have continued to work with local Earlham Computer Science alums who teach as adjuncts periodically. Ray Ontko ('84) and Chris Hardie ('99) are the two we have worked with to-date and plan to continue engaging in the future. The organizations they run are also collectively responsible for the current employment of about 12 Earlham Computer Science graduates; and many more historically. | ||
| + | ===The Teens=== | ||
| + | We conducted the [[Archive:England|England program in 2011]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We moved into the Center for Science and Technology in the fall of 2015. Charlie spoke at the formal opening of the building. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our number of majors continues to grow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As of fall 2019 we have 3 tenured or tenure-track faculty, in addition to one-third of a visiting position in Math/Physics/CS, the post-baccalaureate CS faculty member, and the Math/Physics/CS administrative assistant. We will welcome a new tenure-track faculty member in fall 2020 after a search in 2019-20. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Icelandic Field Studies was wrapped into Earlham's EPIC program and continues to develop more with each cycle. Trips have taken place most years, most recently 2018 and 2019. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Twenties=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 2020, Earlham CS weathered the COVID-19 pandemic by quickly pivoting, along with the whole college, to a remote/hybrid approach to teaching. As of this writing in early 2021, this state of affairs is ongoing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Program and Student Activities== | ||
===Majors and Minors=== | ===Majors and Minors=== | ||
The following charts both the numbers and the moving average of computer science majors, it does not include minors. Although we encourage both science and non-science students to minor in CS, typically there has been no more than one minor per year when there was one. | The following charts both the numbers and the moving average of computer science majors, it does not include minors. Although we encourage both science and non-science students to minor in CS, typically there has been no more than one minor per year when there was one. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 88: | ||
===Applied Groups=== | ===Applied Groups=== | ||
| − | Currently there are | + | Currently there are four applied computer science groups: |
| − | # System and Network Administrators ( | + | # System and Network Administrators (Post-Bac) |
| − | # | + | # Helping Others Program (CS 128/256 instructors) |
| − | + | # Hardware Interfacing Project (Xunfei) | |
| − | # Hardware Interfacing Project ( | + | # Web Dev (Dave) |
| − | # | ||
| − | |||
These groups are collectively responsible for a wide range of hardware and software which the computer science department, and other science departments, depend on daily. The applied groups are a framework which gives us ample opportunities for our students to apply the theories and techniques they learn about in class to real-world problems. Over time we have heard many of our graduates tell us how unique and powerful this aspect of their Earlham education was. | These groups are collectively responsible for a wide range of hardware and software which the computer science department, and other science departments, depend on daily. The applied groups are a framework which gives us ample opportunities for our students to apply the theories and techniques they learn about in class to real-world problems. Over time we have heard many of our graduates tell us how unique and powerful this aspect of their Earlham education was. | ||
| Line 89: | Line 103: | ||
The Computer Science department manages a couple of restricted funds, the most interesting of which is the Computer Science Collaborative Research Fund for Earlham Alumni, Faculty and Students. This fund, while still fairly modest, aims to support research and development projects which involve a slice of people from the Earlham Computer Science landscape. Ultimately we plan to bring alums back to campus periodically to work with current faculty and students as the basis for on-going long-distance collaborations in a variety of areas. | The Computer Science department manages a couple of restricted funds, the most interesting of which is the Computer Science Collaborative Research Fund for Earlham Alumni, Faculty and Students. This fund, while still fairly modest, aims to support research and development projects which involve a slice of people from the Earlham Computer Science landscape. Ultimately we plan to bring alums back to campus periodically to work with current faculty and students as the basis for on-going long-distance collaborations in a variety of areas. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Computing Resources=== |
Over the years the purchase cost of our hardware has been supported by ECS (regular lab upgrades, some servers), donations from Ray Ontko & Company, Sybase Inc, Safe Passage Communications Inc, the employers of a couple of students and recent graduates, grants from the Arthur Vining Davis Foundation, HHMI, and the National Science Foundation, and the scientific equipment fund. | Over the years the purchase cost of our hardware has been supported by ECS (regular lab upgrades, some servers), donations from Ray Ontko & Company, Sybase Inc, Safe Passage Communications Inc, the employers of a couple of students and recent graduates, grants from the Arthur Vining Davis Foundation, HHMI, and the National Science Foundation, and the scientific equipment fund. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 109: | ||
Maple, Gaussian, and WebMO are the only commercial software titles in use on our systems (ECS pays for the former, Chemistry the latter two), otherwise we use open source software for all of our database, web, science, etc. needs so there are no additional licensing costs. | Maple, Gaussian, and WebMO are the only commercial software titles in use on our systems (ECS pays for the former, Chemistry the latter two), otherwise we use open source software for all of our database, web, science, etc. needs so there are no additional licensing costs. | ||
| − | + | Our on-campus users include students and faculty in computer science, chemistry, biology, and mathematics. We support day-to-day, classroom, lab, and student/faculty research activities. Our off-campus users are mostly students and faculty associated with the National Computational Science Institute/SC Education Program. | |
| − | |||
| − | Our on-campus users include students and faculty in computer science, chemistry, biology, and mathematics. We support day-to-day, classroom, lab, and student/faculty research activities. | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| − | |+ Computer Systems Managed by Computer Science [1] | + | |+ Computer Systems Managed by Computer Science Circa 2008 [1] |
|- | |- | ||
! Year | ! Year | ||
| Line 132: | Line 144: | ||
| 25 | | 25 | ||
| 60 | | 60 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2008 | ||
| + | | 7 | ||
| + | | 30 | ||
| + | | 70 | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | [1] All values plus or minus 10% | + | <center>[1] All values plus or minus 10%</center> |
| + | |||
| + | In the 2010s we have taken new steps toward supporting more cloud-style services as part of our workflows. This includes Docker containers as well as hosting many of our tools and services on virtual machines rather than bare-metal hardware. This is in addition to our experience of supporting HPC and parallel-and-distributed cluster computing applications. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:57, 17 February 2025
A Brief History of Computer Science at Earlham College
If you have additions, corrections, etc. you can either edit the page yourself or send them to charliep at cs dot earlham dot edu
The Eighties
In the early 1980s Computer Science was only available as a self-designed major. A couple of courses were taught each year by faculty from physics, mathematics, and Computing Services. Typically a couple of people majored in CS each year, their transcripts included a significant number of independent studies. Charlie, who graduated in 1984, was one of those.
Computer Science became a program with a relatively regular set of course offerings and a defined major in the late 1980s. Faculty from a broad range of departments taught courses along with alums from the area, e.g. Ray Ontko. Ray had taught CS previously when he was working in Computing Services. Ray Hively (Physics) and Hal Hanes (Mathematics) both took intensive summer study courses designed to teach non-computer scientists with a background in science and computing how to teach computer science and then used these new skills to teach a variety of courses in Computer Science.
In general Computing Services supported Computer Science in a variety of ways during this time. George Silver and Larry Fisher both taught courses regularly and served in administrative roles for the program at one point or another along with John Howell, Hal Hanes, and Ray Hively.
One attribute of the major at this time was a requirement to work in Computing Services for a period of time. It was dropped when it became clear there wasn't always a good fit between student's interests and Computing Service's needs.
The Nineties
In the early 1990's staffing Computer Science courses became more and more difficult. Physics, Philosophy, and mostly Mathematics, were contributing more time than they could sustain and adjuncts were hard to coordinate.
In the winter of 1993 Charlie was due for a sabbatical from his software engineering job at Sybase (Sybase is headquartered near Berkeley, CA, Charlie worked from his home South of Richmond). At the same time Earlham needed someone to teach our CS2 course (the first course for potential majors) during the winter term. For the next couple of years Charlie continued to teach a course or so each term and began to work with the first applied computer science group, the System and Network Administrators. Charlie also took on the job of coordinating the Computer Science program.
The 1994 accreditation review identified staffing in Mathematics and CS as a problem. Apparently one of the suggestions of the visiting team was that Earlham might be best served by laying CS down. To their credit, the academic leadership of the College chose to strengthen the program instead.
In the Spring of 1997 the College conducted a formal review of Charlie's teaching and of the Computer Science program. As a result of that review his position was expanded to half-time, tenure track and he was given the title of assistant professor. Additionally he was asked to convene the newly revitalized CS program. His appointment was the first purely computer science position created at Earlham College.
The decade closed with an extraordinary gesture on the part of the Mathematics department when they agreed that the best use of 1/2 of one of their faculty lines would be to combine it with a 1/2 FTE from Computer Science (garnered from pieces of philosophy, physics, and computing services) to create the first full-time, tenure-track position in Computer Science at Earlham.
The Naughts
In 2000 we hired Jim Rogers to fill the new position in Computer Science. At this point our size was 1 (Jim) plus 1/2 (Charlie) plus 1/6 (John Howell) for a total of 1 2/3 FTEs. Among other things Jim brought two important qualities with him, one was an actual graduate degree in computer science (another first at Earlham), another was a strong background in theoretical computer science. Charlie comes from the applied wing of the discipline, prior to Jim's arrival first Hal Hanes, and then Tim McLarnan, provided the theoretical component of the Computer Science program. During our deliberations about the future of the program we realized it was important to preserve this balance. As our first faculty with a Ph.D. in Computer Science Jim also served as an important role model for our students, one they had not had before. His arrival heralded the start of a slow but steady progression of our students pursuing graduate degrees, ultimately even including Charlie who started in 2003.
Up until about 2003 Charlie was often compensated for an additional course for leading the bulk of the applied groups. As Jim began covering some of the groups and Charlie began teaching more this was done away with and they became a part of the fabric of the program.
By the Fall of 2003 the program had grown to the point that we could no longer adequately staff it with 1 2/3 teaching positions. In addition, three of our upper division courses were taught only every three years; we wanted to move these to alternate years and to incorporate the Applied Groups as a regular part of our curriculum. We submitted a request to the Academic Dean to increase our staffing to 2 FTE and return John Howell's 1/6 FTE to Physics.
The 2004 accreditation self-study noted that we had addressed the staffing issues in Math and CS by staffing Math with 3 FTEs and CS with 1.5 FTEs. The subsequent accreditation report noted that "The ratio of numbers of majors to the number of faculty positions in computer science is very impressive. The staffing there is not yet regularized, but Earlham College should think about how to regularize that situation".
That Fall, our proposal was incorporated into the RATS process for the faculty expansion of Fall 2004. This was approved during the Spring of 2005 and was the genesis for Charlie's position moving to full-time.
Also in the Fall of 2004 a review of our status was made, that is are we a program or a department. After a number of conversations and long email messages with Len Clark and others, Len decided that the framework of department best describes Computer Science at Earlham.
In 2003 Jim was granted tenure, in 2006 Charlie was granted tenure. Computer Science continues to be supported with an occasional 1/6 FTE from John Howell in Physics. John has a very long and rich tenure teaching programming and problem solving, our introductory course, and leading the program during the 1980s and early 1990s.
All through the 1990s and 2000s we have continued to work with local Earlham Computer Science alums who teach as adjuncts periodically. Ray Ontko ('84) and Chris Hardie ('99) are the two we have worked with to-date and plan to continue engaging in the future. The organizations they run are also collectively responsible for the current employment of about 12 Earlham Computer Science graduates; and many more historically.
The Teens
We conducted the England program in 2011.
We moved into the Center for Science and Technology in the fall of 2015. Charlie spoke at the formal opening of the building.
Our number of majors continues to grow.
As of fall 2019 we have 3 tenured or tenure-track faculty, in addition to one-third of a visiting position in Math/Physics/CS, the post-baccalaureate CS faculty member, and the Math/Physics/CS administrative assistant. We will welcome a new tenure-track faculty member in fall 2020 after a search in 2019-20.
Icelandic Field Studies was wrapped into Earlham's EPIC program and continues to develop more with each cycle. Trips have taken place most years, most recently 2018 and 2019.
The Twenties
In 2020, Earlham CS weathered the COVID-19 pandemic by quickly pivoting, along with the whole college, to a remote/hybrid approach to teaching. As of this writing in early 2021, this state of affairs is ongoing.
Program and Student Activities
Majors and Minors
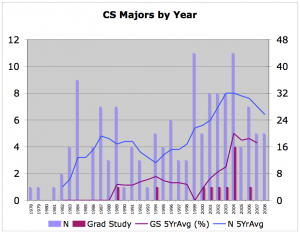
The following charts both the numbers and the moving average of computer science majors, it does not include minors. Although we encourage both science and non-science students to minor in CS, typically there has been no more than one minor per year when there was one.
Graduate Placement
Over the last five or six years EC CS majors have increasingly elected to continue their studies in graduate programs. These include Matt Burke (1989), University of Washington---Mathematics, Dave Hovemeyer (1994), University of Maryland, Alex Reeder (2000), New York University, Ben Bartlet (2001), University of Toronto, Abby Ge (2002) Columbia University---Master of Computational Finance, Josh Hursey (2003) Indiana University, Josh McCoy (2004) University of California Santa Cruz, Seth Hopper (2004) University of North Carolina---Physics, Ian Kelley (2004) University of Delaware, Mikel Rodriquez (2004) University of Central Florida, and Colin Kern (2006) University of Delaware.
Student/Faculty Research
Both Jim and Charlie have organized and now manage student/faculty research groups. Jim's covers his work in computational linguistics and formal language theory and Charlie's works in the areas of high performance computing and computational science. Both groups present posters and papers at national conferences. Jim regularly teaches international workshops during the summer.
Charlie's group also works with a couple of local faculty supporting their research and teaching, John Iverson (Biology) uses our computational facilities to support his work in phylogenetic reconstruction. Lori Watson (Chemistry) uses our gear to support both her research and her teaching. Olen Stephens (Chemistry), Mike Deibel (Chemistry), and Peter Blair (Biology) are all crafting student/faculty research projects for the current HHMI proposal which include significant computational components involving Computer Science students and faculty. Off-campus the Cluster Computing Group is part of the Supercomputing Education Program steering committee and maintains projects with faculty at Stanford (Chemistry and Economics), University of Northern Iowa (Computer Science), UT El Paso (Mathematics), and Lake Forest (Chemistry).
The Keck project includes the development and deployment of computational modules for many introductory and upper-level science classes from a wide range of disciplines (all the sciences except Physics). This will give us new opportunities to work with colleagues here on-campus to develop local computational expertise.
Applied Groups
Currently there are four applied computer science groups:
- System and Network Administrators (Post-Bac)
- Helping Others Program (CS 128/256 instructors)
- Hardware Interfacing Project (Xunfei)
- Web Dev (Dave)
These groups are collectively responsible for a wide range of hardware and software which the computer science department, and other science departments, depend on daily. The applied groups are a framework which gives us ample opportunities for our students to apply the theories and techniques they learn about in class to real-world problems. Over time we have heard many of our graduates tell us how unique and powerful this aspect of their Earlham education was.
Grants and Fundraising
In the late 1990's Computer Science was an integral part of the proposal to the Lilly Foundation that ultimately provided a significant chunk of the funds used to renovate the science complex. We have also secured a number of grants to support equipment purchases and arranged for donations of equipment from the Arthur Vining Davis Foundation, Intel, and Oracle.
We have also played a role, albeit fairly minor, in all three of the HHMI proposals. Computer Science is an integral part of the most recent Keck proposal, working on both field data collection units and curriculum module development. Some of Charlie's on-campus work, and the bulk of his off-campus work, is supported by grants from the National Science Foundation, National Endowment for the Humanities, and the Department of Energy. He and his students play a small part in those grants.
The Computer Science department manages a couple of restricted funds, the most interesting of which is the Computer Science Collaborative Research Fund for Earlham Alumni, Faculty and Students. This fund, while still fairly modest, aims to support research and development projects which involve a slice of people from the Earlham Computer Science landscape. Ultimately we plan to bring alums back to campus periodically to work with current faculty and students as the basis for on-going long-distance collaborations in a variety of areas.
Computing Resources
Over the years the purchase cost of our hardware has been supported by ECS (regular lab upgrades, some servers), donations from Ray Ontko & Company, Sybase Inc, Safe Passage Communications Inc, the employers of a couple of students and recent graduates, grants from the Arthur Vining Davis Foundation, HHMI, and the National Science Foundation, and the scientific equipment fund.
Maple, Gaussian, and WebMO are the only commercial software titles in use on our systems (ECS pays for the former, Chemistry the latter two), otherwise we use open source software for all of our database, web, science, etc. needs so there are no additional licensing costs.
Our on-campus users include students and faculty in computer science, chemistry, biology, and mathematics. We support day-to-day, classroom, lab, and student/faculty research activities. Our off-campus users are mostly students and faculty associated with the National Computational Science Institute/SC Education Program.
| Year | Servers | Clients | Cluster Nodes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 1 | 10 | 0 |
| 1998 | 2 | 15 | 0 |
| 2001 | 4 | 20 | 16 |
| 2004 | 6 | 25 | 32 |
| 2007 | 6 | 25 | 60 |
| 2008 | 7 | 30 | 70 |
In the 2010s we have taken new steps toward supporting more cloud-style services as part of our workflows. This includes Docker containers as well as hosting many of our tools and services on virtual machines rather than bare-metal hardware. This is in addition to our experience of supporting HPC and parallel-and-distributed cluster computing applications.