Sysadmin:New Sysadmins
Welcome to the System Administration ("sysadmin") Applied Group!
Basics
First of all, #include new-member-orientation, which applies to all applied groups.
Check out our Sysadmin reference guide for both Earlham and admin in general. This should include high-level answers to a lot of questions you might have as you dive into your training task list.
Also read this presentation about optimizations in your workflows - software we commonly use, keyboard shortcuts, and more.
Where to ask questions
Share to the group Slack, the mailing list, or the weekly group meeting
- Technical questions of any kind - software, hardware, network, etc.
- Problems you discover with a machine or service
- User questions
- Updates about issues - comments in GitLab auto-post to the admin Slack
- Ideas for new projects (either space works)
Ask the admin faculty supervisor privately in Slack or 1-1 meetings
- Confidential information including passwords
- Delay/absence notifications
- Compensation - pay, credit
- Individual scheduling changes
- Ideas for new projects (either space works)
Training Tasks
This training assumes no background knowledge of System Administration or even the use of Unix-based systems. It is assumed that this shall take you around 2-3 weeks (< 30 hours). As long as you put effort, do what is assigned, and ask questions as needed, you should be on a good track. Do the following, in order:
- Logistical tasks (< 0.5 hr)
- Ask for the creation of user accounts, including CS, Cluster, and Wiki.
- Finish the New Member Orientation mentioned at the beginning of this page. Make sure you have access to Lovelace and Turing labs, at least.
- Vim Training. Vim is a commonly used editor for many admin tasks. Hence, learning this editor is important. Dedicate around an hour for this task.
- Open a terminal or connect to Bowie via your Windows terminal of choice.
- After logging in with your CS account, open the terminal, type
vimtutor, and press enter. Follow the instructions.
- Familiarize yourself with the Earlham Admin environment. Read the following and ask questions: (< 1 hr)
- Go on a server room tour. Another SysAdmin can help you with this. Take a look at the servers, ask questions, try to find machines that you are familiar with. Consider the diagram you looked at. Ask questions about where things are and how they are connected/why.
- Unix Training. For this part, you will need a terminal/unix environment. It is recommended that you do this on a Linux system. Our servers are a good place for this part. Navigate to Unix Lesson and attempt the first setup and first three sections, until and including working with files and directories). Ask questions, and don't get stuck. You don't need to read everything here. Just skim through these lessons and get a decent understanding. This should take approx. 2 hours. If you're spending more than 3 hours on this, please reach out to us asap.
- Now you're ready for something more exciting. Let's get to ssh-key setup. You should by now know what ssh is. If not, navigate to the reference guide.
- (Optional) If you want to read more about ssh-keys, navigate here.
- Use this tutorial to set up ssh-keys for CS (tools) and Cluster (hopper) on your machine. You will need a Unix environment for this.
- Modify your SSH config file (.ssh/config in your home directory). This file can be used to simplify the process of jumping around between machines. Example:
- Host whedon
- Hostname whedon.cluster.earlham.edu
- User sysadmin
- Host _whedon
- Hostname whedon.cluster.earlham.edu
- User [username]
- Host whedon
- Finish sections 4 and 5 of the Unix Lesson. This should take approx 2 hours.
- Test your knowledge: (~30 minutes). There is a file on each node of hamilton:
/home/sysadmin/sysadmin-training/h_message.txt
Write a bash for loop that prints all these messages in order. (from hamilton0). - Finish sections 6 and 7 of the Unix Lesson. This should take approx 2 hours.
- Start on Project 0 (Should take a few weeks, depending on weekly hours).
Project Zero (Created 2023, Updated Jan 2024)
Note: You will be given a lab machine to work on, a USB drive for installing an OS, and an IP and Hostname to use.
- Create a bootable USB with Debian Linux on it.
- Install Debian on your project machine.
- Plug in your USB drive, and start up the computer. As the computer starts, hit the F9 key (this varies from machine to machine, but the system will usually offer some information on the boot splash screen as to how to access the BIOS menu) to bring up the menu. Navigate to the boot options, and select your USB drive. If everything up to this point has worked correctly, you should see a Debian logo and a menu offering different installation options.
- Choose
graphical install. - Choose English, US, American (makes commands match documentation, etc)
- Choose Configure Network Manually
- Address: [given address]
- Netmask: 255.255.255.0
- Gateway: 159.28.22.254
- DNS Server: 159.28.22.1
- Choose an appropriate hostname
- The domain name is cs.earlham.edu
- Create a root password. Make sure it is secure and memorable.
- Create a user account with the following information:
- Username: sysadmin
- Password: <choose-something-secure-and-memorable>
- Choose the US-Eastern time zone.
- For disk partitioning choose Guided, use entire disk
- Choose drive sda
- Choose all files in 1 partition
- Write changes to disk
- Choose No Network Mirror, No Popularity
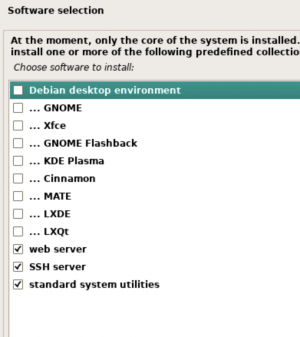
- Choose the following packages:
- Install GRUB as the boot manager on /dev/sda
- At the end of the installation, it will ask you to remove the USB drive and reboot.
- Configure the system
- Log in and use the
sucommand to switch to the root account, you will need this in order to edit/configure the system. - Test your network connection by pinging a Google server:
ping 8.8.8.8. If things aren't working, check out/etc/network/interfaces. This file contains all the configuration for your network connection. There is an example of what this file might look like below. You may have to restart the network package, or just restart the computer before the configuration takes effect.- Use the following network settings:
- Address:
[given address] - Netmask:
255.255.255.0 - Gateway:
159.28.22.254 - DNS Server:
159.28.22.1
- Address:
- Use the following network settings:
- Log in and use the
- Install/configure sudo. Add your sysadmin user to the config so that they can run any command. In general, you should log in as yourself or sysadmin and then use sudo "command" when you want to be root.
- Configure drive mounts (you will need root or sudo for this)
sudo apt-get install nfs-common- install dependencies- Create /eccs and /clients directories in /
- edit the file
/etc/fstabto include the following lines (these are our shared drives for users):159.28.22.5:/earlhamcs/clients /clients nfs auto 0 2159.28.22.5:/earlhamcs/eccs /eccs nfs auto 0 2
- Use the command
sudo mount -ato reload the configuration. It should run quickly. You can make sure it worked by checking that/eccsnow has files/folders in it.
- Set up the following services:
- An apache2 server, including a public HTML page with �Hello, World!�.
- An openssh server.
- Git CLI.
- Docker, including a docker container of your choice, or the docker | "hello world" image.
- SSH - on your local Linux machine, or another configured lab machine (at least one should be usable, check with Porter):
- create ssh keys for your Project 0 machine.
- Copy the public key to your Project 0 machine.
sshfrom the Linux machine to the Project 0 machine using keys.- follow the same process and ssh from the Project 0 machine to the CS domain (Bowie) using keys for authentication.
- Email the admin list (
admin@cs.earlham.edu) to announce completion.
Ask questions
If that all seems like a lot, ask questions. These steps are designed to expose you to our infrastructure, tools we commonly use (including the wiki and email list), patterns we follow, and building blocks of more complex administrative tasks.
Obtain keys
Key form is here, request:
- Noyes basement, CAB 13
- Server room if applicable, CAD 3
You'll need a relevant faculty member (typically your applied group supervisor) to approve your request.
Public Safety should contact you when your keys are ready.
Examples
Network Interfaces Example
auto eno1
allow-hotplug eno1
iface eno1 inet static
address 159.28.22.11
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 159.28.22.254
dns 159.28.22.1