Difference between revisions of "HIP:Mashup"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
* GNUplot which is used to get the graph is installed in all the ACLs and in stewie, and hence you don't have to install to use it.<br> | * GNUplot which is used to get the graph is installed in all the ACLs and in stewie, and hence you don't have to install to use it.<br> | ||
* To make the graph, go to the directory where you have your data file (which will be a csv file if it was generated by EcoWatch).<br> | * To make the graph, go to the directory where you have your data file (which will be a csv file if it was generated by EcoWatch).<br> | ||
| − | *type "gnuplot" and return | + | *Into that directory, copy the following script and make adjustments for the name of your data file and the the ranges for your parameters. |
| − | *To plot the data file type 'load "file name" | + | *type "gnuplot" and return.<br> |
| + | *To plot the data file type 'load "script name"' and enter.<br> | ||
| + | *Here is the script: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/usr/local/bin/gnuplot] | ||
| + | reset | ||
| + | set terminal x11 | ||
| + | #set output "aaa.png" | ||
| + | set datafile separator "," | ||
| + | set xdata time | ||
| + | set timefmt "%H:%M:%S" | ||
| + | set xrange ["11:20:50":"11:38:00"] | ||
| + | set format "%H:%Mam" | ||
| + | set title "Springwood Lake\nMay 25, 2009" | ||
| + | set multiplot | ||
| + | unset ytics | ||
| + | plot [][22:24] "MIK2.csv" using 2:3\ | ||
| + | notitle with p lt rgb "red" pt 2 #Temp | ||
| + | plot [][600:650] "MIK2.csv" using 2:4\ | ||
| + | notitle with p lt rgb "yellow" pt 4 #Cond | ||
| + | plot [][0:100] "MIK2.csv" using 2:8\ | ||
| + | notitle with p lt rgb "green" pt 6 #ORP | ||
| + | plot [][9.6:10.65] "MIK2.csv" using 2:7\ | ||
| + | notitle with p lt rgb "blue" pt 8 #pH | ||
| + | set key bottom left | ||
| + | set key box lt 5 lw 2 | ||
| + | replot "MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\ | ||
| + | title "Temperature(22-24C)" with p lt rgb "red" pt 2,\ | ||
| + | "MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\ | ||
| + | title "Conductivity(600-650uS/cm)" with p lt rgb "yellow" pt 4,\ | ||
| + | "MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\ | ||
| + | title "ORP(0-100mv)" with p lt rgb "green" pt 6,\ | ||
| + | "MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\ | ||
| + | title "pH(9.6-10.65)" with p lt rgb "blue" pt 8 | ||
| + | unset multiplot | ||
| + | |||
| + | #EOF | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | *Next you want to get a satellite picture showing exactly where you took you data. To get this, you have to go to the directory where you have you data file from the YSI 650 MDS. | ||
| + | *Copy the following perl script into the same directory. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/usr/bin/perl | ||
| + | #Written by: Mikio Takizawa | ||
| + | #July 2008 | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | #Modified in May 2009 | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | #This script is for converting csv file, which is the data from | ||
| + | #springwood database, to kml file. | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | #Sample basic structure of kml file | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | #<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> | ||
| + | #<kml xmlns="http://earth.google.com/kml/2.2"> | ||
| + | # <Placemark> | ||
| + | # <name>Simple placemark</name> | ||
| + | # <description>Attached to the ground. Intelligently places itself | ||
| + | # at the height of the underlying terrain.</description> | ||
| + | # <Point> | ||
| + | # <coordinates>-122.0822035425683,37.42228990140251,0</coordinates> | ||
| + | # </Point> | ||
| + | # </Placemark> | ||
| + | #</kml> | ||
| + | |||
| + | use strict; | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ARGV[1] or die "Usage: $0 <infile> <outfile>\n"; | ||
| + | |||
| + | my $infile = $ARGV[0]; | ||
| + | my $outfile = $ARGV[1]; | ||
| + | my $i; | ||
| + | my $j; | ||
| + | my $k; | ||
| + | my $l; | ||
| + | my $sdate; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | *Run the scrip on you data file and send the out put to an output file. | ||
| + | *eg: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$ ls | ||
| + | MIK2.csv sanele2.kml ysi650_2_kml.pl ysi650_2_plot.gplot | ||
| + | wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$ perl ysi650_2_kml.pl MIK2.csv sanele3.kml | ||
| + | Choose date from: "Date" "M/D/Y" "05/25/09" | ||
| + | Which one?: "05/25/09" | ||
| + | "05/25/09" | ||
| + | sanele3.kml is ready. | ||
| + | wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$ | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | *Copy the kml file to your www directory in you home directory on quark. | ||
| + | *Copy that same file from your www directory onto your desktop. | ||
| + | *Now you can open google earth drag the file from your desktop and drop it on google earth. | ||
| + | *Sometimes you might have to zoom into the picture to see it clear (it will be indicated by a pin(s). | ||
| + | *There are a number of way which can be used to copy the picture from google earth to your desktop. | ||
| + | * One of them, which is the one I used is taking a snap shot of my desktop using the splat key + 4 on my apple computer. | ||
| + | *That picture is now ready to be integrated with the gnuplot we made using the GNUplot software. | ||
| + | *To Do the integration we use the GNU Image Manipulation Program mentioned above. | ||
| + | *Before doing that however, lets look into another way of getting our kml file into a satellite picture. | ||
| + | *We are going to use google maps instead of google earth. | ||
| + | *In this case you go to google maps. In the search bar, type "http://cs.earlham.edu/~stmahla07/sanele2.kml" enter ( substitute stmahla07 for earlham username(home directory on quark) and sanele2.kml for file name). <br> | ||
| + | *Here you will get something similar to what google earth will give you. And again, you can copy the image onto your desktop in a number of ways including taking a snapshot of your desktop. | ||
| + | **Doing the real Mashup! | ||
--to be continued. | --to be continued. | ||
Revision as of 17:55, 3 June 2009
Getting to the final mashup
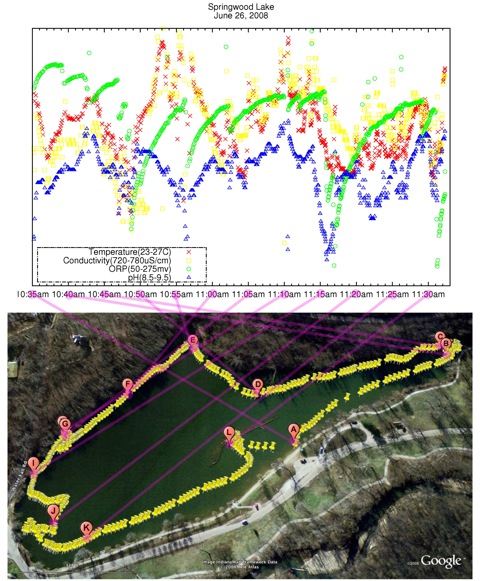
This is an easy step by step procedure for converting data collected by sonde into the YSI 650 MDS and transfered into a computer to the pictures as seen below.
The following is an example of data from sonde, which has been converted to a csv file using EcoWatch.
"Date","Time","Temp","SpCond","Cond","Resistivity","pH","ORP","Longitude","Latitude" "M/D/Y","hh:mm:ss","C","uS/cm","uS/cm","Ohm.cm","","mV","DD.dddd","DD.dddd" "05/25/09","11:20:54",23.13,614.0,592.0,1688.4,8.98,145,-84.899391,39.848564 "05/25/09","11:21:04",23.14,616.0,594.0,1682.3,8.97,24,-84.899391,39.848560 "05/25/09","11:21:14",23.16,618.0,596.0,1677.6,8.92,10,-84.899406,39.848568 "05/25/09","11:21:24",23.23,616.0,596.0,1679.0,9.13,-8,-84.899414,39.848614 "05/25/09","11:21:34",23.30,615.0,595.0,1682.0,9.71,-3,-84.899445,39.848648 "05/25/09","11:21:44",23.31,614.0,594.0,1682.8,10.10,7,-84.899544,39.848686 "05/25/09","11:21:54",23.29,614.0,594.0,1683.5,10.28,14,-84.899628,39.848701 "05/25/09","11:22:04",23.21,615.0,594.0,1684.6,10.37,20,-84.899734,39.848736 "05/25/09","11:22:14",23.14,617.0,595.0,1681.2,10.38,24,-84.899818,39.848812 "05/25/09","11:22:24",23.09,617.0,595.0,1680.9,10.41,28,-84.899948,39.848873 "05/25/09","11:22:34",23.01,620.0,596.0,1677.1,10.39,32,-84.900017,39.848980
The final product from the cvs file is presented as the pictures below, which was produced from a combination of google earth, GNUplot and GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP).
- GNUplot which is used to get the graph is installed in all the ACLs and in stewie, and hence you don't have to install to use it.
- To make the graph, go to the directory where you have your data file (which will be a csv file if it was generated by EcoWatch).
- Into that directory, copy the following script and make adjustments for the name of your data file and the the ranges for your parameters.
- type "gnuplot" and return.
- To plot the data file type 'load "script name"' and enter.
- Here is the script:
#!/usr/local/bin/gnuplot]
reset
set terminal x11
#set output "aaa.png"
set datafile separator ","
set xdata time
set timefmt "%H:%M:%S"
set xrange ["11:20:50":"11:38:00"]
set format "%H:%Mam"
set title "Springwood Lake\nMay 25, 2009"
set multiplot
unset ytics
plot [][22:24] "MIK2.csv" using 2:3\
notitle with p lt rgb "red" pt 2 #Temp
plot [][600:650] "MIK2.csv" using 2:4\
notitle with p lt rgb "yellow" pt 4 #Cond
plot [][0:100] "MIK2.csv" using 2:8\
notitle with p lt rgb "green" pt 6 #ORP
plot [][9.6:10.65] "MIK2.csv" using 2:7\
notitle with p lt rgb "blue" pt 8 #pH
set key bottom left
set key box lt 5 lw 2
replot "MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\
title "Temperature(22-24C)" with p lt rgb "red" pt 2,\
"MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\
title "Conductivity(600-650uS/cm)" with p lt rgb "yellow" pt 4,\
"MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\
title "ORP(0-100mv)" with p lt rgb "green" pt 6,\
"MIK2.csv" using 1:(1/0)\
title "pH(9.6-10.65)" with p lt rgb "blue" pt 8
unset multiplot
#EOF
- Next you want to get a satellite picture showing exactly where you took you data. To get this, you have to go to the directory where you have you data file from the YSI 650 MDS.
- Copy the following perl script into the same directory.
#!/usr/bin/perl #Written by: Mikio Takizawa #July 2008 # #Modified in May 2009 # #This script is for converting csv file, which is the data from #springwood database, to kml file. # # #Sample basic structure of kml file # #<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> #<kml xmlns="http://earth.google.com/kml/2.2"> # <Placemark> # <name>Simple placemark</name> # <description>Attached to the ground. Intelligently places itself # at the height of the underlying terrain.</description> # <Point> # <coordinates>-122.0822035425683,37.42228990140251,0</coordinates> # </Point> # </Placemark> #</kml> use strict; $ARGV[1] or die "Usage: $0 <infile> <outfile>\n"; my $infile = $ARGV[0]; my $outfile = $ARGV[1]; my $i; my $j; my $k; my $l; my $sdate;
- Run the scrip on you data file and send the out put to an output file.
- eg:
wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$ ls MIK2.csv sanele2.kml ysi650_2_kml.pl ysi650_2_plot.gplot wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$ perl ysi650_2_kml.pl MIK2.csv sanele3.kml Choose date from: "Date" "M/D/Y" "05/25/09" Which one?: "05/25/09" "05/25/09" sanele3.kml is ready. wir059151:untitled folder sanelemahlalela$
- Copy the kml file to your www directory in you home directory on quark.
- Copy that same file from your www directory onto your desktop.
- Now you can open google earth drag the file from your desktop and drop it on google earth.
- Sometimes you might have to zoom into the picture to see it clear (it will be indicated by a pin(s).
- There are a number of way which can be used to copy the picture from google earth to your desktop.
- One of them, which is the one I used is taking a snap shot of my desktop using the splat key + 4 on my apple computer.
- That picture is now ready to be integrated with the gnuplot we made using the GNUplot software.
- To Do the integration we use the GNU Image Manipulation Program mentioned above.
- Before doing that however, lets look into another way of getting our kml file into a satellite picture.
- We are going to use google maps instead of google earth.
- In this case you go to google maps. In the search bar, type "http://cs.earlham.edu/~stmahla07/sanele2.kml" enter ( substitute stmahla07 for earlham username(home directory on quark) and sanele2.kml for file name).
- Here you will get something similar to what google earth will give you. And again, you can copy the image onto your desktop in a number of ways including taking a snapshot of your desktop.
- Doing the real Mashup!
--to be continued.