Difference between revisions of "3D Printing"
m (→Lulzbot Taz 5) |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Following is a detailed description of how to use the 3D printers located in Babbage. Currently, the Lulzbot Taz 5 is the only printer in working order. The process starts with a design in an STL file format. The computers in Babbage are equipped with OpenSCAD software, as well as Fusion 360. however, any design software can be used as long as the file is exported in an .stl format. For the Lulzbot Taz 5, Cura is used to preparing the design for printing and control the printer. The actual printing takes a long time and requires a lot of patience especially when ensuring a good first layer. Sit down to print with a mind open to repeated failure, only then will you be able to achieve a successful print worthy of your time and the resources used. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == '''Introducing our 3D printers:''' == | |
| − | |||
| + | {|style="margin: 0 auto;" | ||
| + | |[[File:MakerBot.jpg|thumb|300px|MakerBot]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Robo_3D.jpg|thumb|300px|Robo 3D]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Taz_LulzBot.jpg|thumb|300px|Taz Lulzbot]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | == '''Printing instructions:''' == | ||
| − | |||
| − | 3D | + | === '''Instructions on how to use the 3D printers:''' === |
| − | '''ReplicatorG''' | + | |
| + | ==== '''Lulzbot Taz 5''' ==== | ||
| + | Software for the printer: Cura | ||
| + | |||
| + | Steps for printing: | ||
| + | *turn on the printer using the power switch on the Lulzbot | ||
| + | *open Cura, click on the "monitor" tab and click "connect" located about halfway down the sidebar in the controls section | ||
| + | *once the printer is connected preheat the nozzle and the bed by clicking "preheat" the nozzle will automatically preheat to 245deg C, the bed has a default of 75deg C but should be set to preheat at 90deg C | ||
| + | *while the printer is preheating go to the "prepare tab" and open your design file | ||
| + | *scale and position the design making sure it will print in a stable position (usually it will do this automatically) | ||
| + | *If there are any dramatic overhangs in the design, click the "generate support" box, Cura will generate supports for those parts of the model which are thin enough that they can be removed after the design is printed | ||
| + | *selecting a base type is subjective based on the model, if it is unbalanced it may need it. It is recommended to at least use the "skirt" base option, this prints a circle around the model. This is helpful because often the extruder does not function perfectly when it first starts printing due to the polymer building up in the nozzle | ||
| + | *once you have prepared the design click on the monitor tab and click "start print" at the bottom of the sidebar | ||
| + | *adjust the knob on the printer to lower the print speed to 50% to ensure a good first layer | ||
| + | ** you may have to use the tweezers to pull off melted filament from the nozzle if it starts to build up as the printer is running through its preperation steps before it starts printing the design | ||
| + | *watch to ensure a solid first layer then the knob on the printer can be adjusted to 100% speed | ||
| + | *once the printer has completed a few layers and you are content with the initial results you should be able to sit back and let the printer work its magic | ||
| + | *the printer can be left unattended while printing but should be checked on periodically | ||
| + | *let the bed cool to around 50deg before removing the print | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===='''troubleshooting the first layer'''==== | ||
| + | The first layer is important to ensure a good final print and to make sure the printer is functioning correctly. If there are minor issues with the first layer you can keep watching and see if the subsequent layers cover up the errors sufficiently. However, if there are major problems you should abort the print, scrape off what was printed on the build plate with the plastic spatula, and start over. The build plate and nozzle will have to reheat again but they should still be close to the desired temperature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the filament is not extruding properly | ||
| + | *abort the print | ||
| + | *go to the controls section and rise the extruder a little bit off the build plate by clicking the up arrow for the z-axis several times | ||
| + | *using the tweezers pull off any built-up filament form the tip of the extruder | ||
| + | *next, click "extrude" 5-15 times until the filament is flowing correctly from the nozzle/extruder (note: it is a little delayed so filament will not immediately come out right when you click extrude" | ||
| + | *remove the printed material from the build plate | ||
| + | *start the print again | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the filament is extruding properly but not adhering to the build plate | ||
| + | *abort the print | ||
| + | *remove the printed material from the build plate | ||
| + | *if a glue stick is available, apply to the area of the build plate where the design will be printed | ||
| + | *alternatively, you could try wiping the build plate down with a paper towel with some alcohol on it (there should be some isopropyl alcohol on the shelves above the Lulzbot) | ||
| + | *start the print again | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Robo R1+ 3D Printer''' ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Software for the printer: MatterControl | ||
| + | |||
| + | Printing from an SD card: | ||
| + | *Insert a microSD card into the Mac and get rid of any files in it. | ||
| + | *Open MatterControl and drag your .stl file into the QUEUE section of the application. | ||
| + | *On the top-left section, click on “Select Printer.” Select “Robo 3D TM Turing” in the window that pops out. | ||
| + | *Towards the bottom of the QUEUE section, you will find a “Queue” button. Click on it to get a list. | ||
| + | *On the list, below GCode, select “Export to Folder or SD Card.” Click on the microSD card under “Devices” in the side panel and click on “Export” | ||
| + | *Now, in Finder, browse to the microSD card and rename the file you just exported as “auto0.g” (auto zero dot g). Choose “Use.g” if a prompt appears. | ||
| + | *Then, safely remove the microSD card from the Mac and insert it into the Robo 3D printer. | ||
| + | *Prep the build plate using one the following: | ||
| + | **Glue Stick | ||
| + | **Vinyl Sheeting | ||
| + | **Hairspray | ||
| + | :Apply whichever product on the surface of the build plate enough to cover the surface you will be printing on. | ||
| + | *Turn the printer on. Your print will start after about 5 minutes. | ||
| + | *After the print is over, wait for the temperature to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object from the build plate. | ||
| + | *Clean the build plate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Printing from the computer: | ||
| + | *Open MatterControl and drag your .stl file into the QUEUE section of the application. | ||
| + | *On the top-left section, click on “Select Printer.” Select “Robo 3D TM Turing” in the window that pops out. | ||
| + | *Under "Settings" ensure that the correct material is selected. | ||
| + | *Under "Controls" an offset of 0.9 typically shows the best results. | ||
| + | *Pre-heat the extruder and bed on the same page. | ||
| + | *Alternatively, near the top center of the screen, an extruder temperature and a bed temperature will be shown, mouse over and click "pre-heat" for both. | ||
| + | *Prep the build plate using one the following: | ||
| + | **Glue Stick | ||
| + | **Vinyl Sheeting | ||
| + | **Hairspray | ||
| + | *Click print once the printer has heated up. | ||
| + | *After the print is over, wait for the temperature to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object from the build plate. | ||
| + | *Clean the build plate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''MakerBot 3D Printer''' ==== | ||
| + | Software for the printer: ReplicatorG | ||
| + | |||
| + | Steps to follow in order to print: | ||
| + | *Insert a microSD card into the Mac. | ||
| + | *Open ReplicatorG, drag and drop your stl file into application screen. | ||
| + | *Adjust your model if you need to. | ||
| + | *Select “Generate GCode” on the bottom right. | ||
| + | *Make sure the values are set as shown in the image below and then select “Generate GCode” | ||
| + | :[[File:Replicator_values.png|thumb|250px|center]] | ||
| + | *If prompted with an “Acceleration Warning” select “OK” | ||
| + | *Wait until it generates the gcode. | ||
| + | *After the file is generated go to the gcode tab and modify the numbers on the lines M104 should be 230 and M109 should be 128, i.e.: | ||
| + | :M104 S230 T1 (set extruder temperature) M109 S128 T1 (set HBP temperature) | ||
| + | :Make sure to save it by pressing “Command + S”. | ||
| + | *Select “Build to file using SD Card” as shown in the image below. Select the microSD card and make sure to save it as “.x3g” format. | ||
| + | :[[File:Build_from_sd.png|thumb|300px|center]] | ||
| + | *Wait until it is done building and then safely eject the sdCard from the Mac and insert it into the MakerBot. Note: You can find the sdCard slot as shown in the image below: | ||
| + | :[[File:MakerBot-slot.jpg|thumb|300px|center]] | ||
| + | *Turn on the printer. | ||
| + | *Select “Build from SD” and then using the arrows scroll down to your file. | ||
| + | *The printer will start heating up and once it finishes heating up, it will start printing. | ||
| + | *Once the printing has finished, wait for the bed to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =Introduction Pegasus Touch Laser SLA 3D Printer= | ||
| + | |||
| + | The SLA printer currently being used in the display case in Dennis is a Pegasus Touch by FSL3D. The Pegasus Touch prints with a clear Photopolymer resin, and has a build volume of 7”x7”x9” (177x177x228mm). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==FSL3D Resources== | ||
| + | |||
| + | See below for a number of helpful resources for operating the Pegasus Touch provided by FSL3D: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/pegasus-touch/ Pegasus Touch product page and full system specs] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://fsl3d.wikispaces.com/ FSL3D Wiki space and Pegasus Touch user manual] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/downloads/ FSL3D Software and manual downloads] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Safety== | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are a number of safety hazards involved in the operation of the Pegasus Touch. Please exercise caution and take note of the guidelines below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Work Area=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The printer must be installed on a level surface in order to prevent resin spillage. It should also be kept away from direct sunlight, as this can interfere with the printing process and effect the resin being used. Although the printer does not emit any fumes, a well-ventilated area should be identified for using isopropyl alcohol to finish printed parts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Photopolymer Resin=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Photopolymer resin is irritating to the eyes, respiratory system and skin. Direct contact with the liquid resin should be minimized, and exposed skin should be washed thoroughly after handling. It is advisable to use impermeable, chemical-resistant gloves when handling the resin, and safety goggles or glasses if possible. Resin containers should remain sealed, and the opening of the Pegasus Touch should be kept to a minimum while there is resin in the build area. In addition, resin should not be allowed to drip into the Pegasus Touch outside of the build area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before handling the resin, see: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/?wpdmact=process&did=NC5ob3RsaW5r MSDS for Resin] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Laser Safety=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The printer should remain CLOSED while operating. The autolock should only be overridden in the case of an emergency, and only with proper eye protection. Opening the printer during a job, without pausing it, can expose you to class 3B laser radiation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Setup== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ensure that the machine is properly connected: | ||
| + | **The ethernet port on the machine connects to the nearby freeport on the wall. | ||
| + | **The power adapter plugs into the nearby power outlet on the wall. | ||
| + | **The DC barrel connector plugs into the power port on the machine. | ||
| + | **If turned off, the machine should boot within 90 seconds of being properly connected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ensure that the build head and resin vat are securely fastened and leveled. If the build head and vat are not securely fastened and leveled, refer to the discussion of the procedure in the maintenance section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ensure that the build head has been properly cleared of all resin remaining from previous prints. If resin remains on the build head, refer to the discussion of cleaning the build head in the post-production section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ensure that you have access to isopropyl alcohol (or a similar alcohol), a safe container to use, and chemical-resistant gloves for the finish process | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fill the vat with resin up to the minimum fill line, or the first step. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Printing== | ||
| + | |||
| + | To print from the Pegasus Touch, first download FSL3D's RetinaCreate software and ensure a secure internet connection: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/?wpdmact=process&did=MS5ob3RsaW5r Download RetinaCreate Software Windows Vista – 8.1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/?wpdmact=process&did=Mi5ob3RsaW5r Download RetinaCreate Software Mac OS X 10.9 *ALPHA PREVIEW*] | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: The OS X version of the software is EXTREMELY minimal. Thus far we have not had success in using it to print on the Pegasus Touch. Therefore is is highly recommended that you use RetinaCreate for Windows. This has not been done successfully yet, and the only prints created with the Pegasus Touch have been test prints that come pre-loaded on the device. If you experiment with the Windows version of the software, please document your experience here. A good guide can be found [http://fsl3d.wikispaces.com/Part+6+-+Retina+Create here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Resin=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | If needed, more resin may be added the vat during a print. To do this, make sure that you pause the print using the LCD interface before opening the printer to add more resin. Do not add resin up to the maximum fill line until at least 10cm of printing has been completed, so that it does not overflow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Post-Production== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *When the model has finished, wait at least 10 minutes to allow excess resin to drip into the vat before opening the lid. | ||
| + | *It is recommended that you insert a cutting board or other safe surface on top of the vat before removing the build head. This is to prevent excess resin from dripping into the machine. | ||
| + | *Remove the build platform by unscrewing the fastening bolt, gently sliding it out, and flipping it over once it is out of the printer. | ||
| + | *Scrape any excess resin back into the vat before taking the model to an acceptable finish station. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: finished parts may remain on the build platform form up to several days as long as the lid is left shut and the printer is kept out of direct contact with UV sunlight. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Finishing steps=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Scrape or pull the model(s) off of the build platform (ensure that you are using gloves to prevent direct skin exposure to the resin). | ||
| + | *Place the model(s) into a safe container and submerge them in isopropyl alcohol or a similar alcohol for 15 minutes. | ||
| + | *Remove the model(s) from the alcohol and carefully remove the support structure. | ||
| + | *Rub the build platform with IPA, rinse and dry before replacing it. | ||
| + | *If there is still resin in the printer's vat, make SURE that the lid of the Pegasus Touch remains closed after you are done. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Maintenance== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A number of maintenance procedures must be periodically performed to ensure that the Pegasus Touch continues to move smoothly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Build plate leveling=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The build plate should be re-leveled if the build plate and the bottom of the vat are not properly aligned, or if the Pegasus Touch is ever physically moved. A video tutorial that outlines this process may be found here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.fsl3d.com/video-tutorials/ FSL3D video tutorials] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Motor calibration=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The motor may be manually calibrated if necessary. This will reset the starting z-position of future prints, and should be done if the Pegasus Touch is moved or exposed to significant temperature changes. To manually calibrate the motor, navigate the LCD display to the motor calibration screen and lower the build plate using the ‘Motor Down’ button until it nearly touches the vat. Then, finely adjust the build plate level by opening the case and twisting the lead screw manually. The goal is to leave less than 0.5mm of space between the build plate and the vat. Once this is accomplished, press the ‘Set Motor Homing’ button. The motor will then raise the build plate a few centimeters automatically. Verify that the homing has been set accurately by pressing the ‘Test Motor Homing’ button and seeing that the build plate returns to the position hovering slightly above the vat. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Laser calibration=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have yet to perform laser calibration. Please update this page with your experiences if you calibrate the laser. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Introduction MakerBot Replicator= | ||
| + | |||
| + | The printer currently being used in the physics lab Dennis 128 is a MakerBot Replicator. The Replicator can print both ABS and PLA filament, and has a build volume of 8.9" L x 5.7" W x 5.9" H. ((255x145x150mm) It also comes equipped with a dual extrusion system to be able to print objects in two colors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://store.makerbot.com/replicator.html#specifications Makerbot Replicator product page and full system specs] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Software== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A very user-friendly program to use to communicate with the Replicator is MakerBot's own ReplicatorG, which can be found as a free download here: http://replicat.org/download. There are installation instructions included on that website, as additional downloads are required (Python and some drivers). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === '''Desiging your own 3D model:''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Cheat Sheet: http://www.openscad.org/cheatsheet/index.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | After creating your own 3D model follow these steps: | ||
| + | * Render and compile your code by pressing F6 | ||
| + | * Export the design as .stl | ||
| + | * If the file is in your own computer, move the file(name.stl) to the Mac found in Turing lab(CST 222) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | All programs mentioned are free. | ||
| + | ==OpenSCAD== | ||
| + | Open source. Programmatic 3d modeling. Very precise, units in millimeters. | ||
| + | ===Preparing a model in OpenSCAD for printing=== | ||
| + | *You’ll need: | ||
| + | **http://replicat.org/ | ||
| + | **http://www.openscad.org/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | After creating your own 3D model follow these steps: | ||
| + | * Render and compile your code by pressing F6 | ||
| + | * Export the design as .stl | ||
| + | * If the file is in your own computer, move the file(name.stl) to the Mac found in Turing lab(CST 222) | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the pegasus printer | ||
| + | *open that stl in ReplicatorG | ||
| + | *center the object and put on platform if necessary | ||
| + | generate gcode | ||
| + | *recommended settings: left extruder, 15% infil, .20 layer height, 35 extruder and motor speed | ||
| + | *Wait. | ||
| + | *After the file is generated go to the gcode tab and modify the numbers on the lines M104 should be 230 and M109 should be 128, i.e.: | ||
| + | <code>M104 S230 T1 (set extruder temperature)</code> | ||
| + | <code>M109 S128 T1 (set HBP temperature)</code> | ||
| + | *export file to disk | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Blender== | ||
| + | Open source. The best open source modeler out there, very powerful, hard to get to be precise for engineering centric designs. After exporting a model to an .stl you'll want to run the model through [http://www.netfabb.com/ Netfabb] which will check to make sure the model has no holes or connected meshes that share a single edge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Google SketchUp== | ||
| + | Maintained by Google, tutorials available. | ||
| + | ==Thingiverse== | ||
| + | 3D models can be uploaded and downloaded online through a free website called [http://www.thingiverse.com Thingiverse]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==ReplicatorG== | ||
ReplicatorG is the main interface between the 3D model and the printer. Since 3D models are usually .cad, .obj, or .stl files, the printer cannot directly print them. ReplicatorG uses a tool called Skeinforge to take the 3D model as a .stl file, and turn it into gcode. Skeinforge slices the model into layers and determines what paths the extruder needs to take for each layer based on the parameters set in ReplicatorG. The resulting file is a .gcode file, which can be printed directly from the computer if connected via USB. To print without connecting a computer, the .gcode file needs to be converted to a .s3g file and saved to an SD card, as discussed below. | ReplicatorG is the main interface between the 3D model and the printer. Since 3D models are usually .cad, .obj, or .stl files, the printer cannot directly print them. ReplicatorG uses a tool called Skeinforge to take the 3D model as a .stl file, and turn it into gcode. Skeinforge slices the model into layers and determines what paths the extruder needs to take for each layer based on the parameters set in ReplicatorG. The resulting file is a .gcode file, which can be printed directly from the computer if connected via USB. To print without connecting a computer, the .gcode file needs to be converted to a .s3g file and saved to an SD card, as discussed below. | ||
| − | + | ==Interface== | |
| − | ReplicatorG will display a 3D interactive preview of the open .stl file. The column on the right offers some options on how to orient the model on the actual build platform. Some of these options include moving, rotating, or scaling the model before it is printed. It has default "snap-to" settings to center the model on the platform, and move it so that its bottom most side (the first layer) is laying just on the surface of the build platform. A model that lies below the build platform will result in an error and will not print correctly, and a model that lies above the platform will print with severe warping, since the first layer of plastic will have nothing on which to adhere. | + | ReplicatorG will display a 3D interactive preview of the open .stl file. The column on the right offers some options on how to orient the model on the actual build platform. Some of these options include moving, rotating, or scaling the model before it is printed. It has default "snap-to" settings to center the model on the platform, and move it so that its bottom-most side (the first layer) is laying just on the surface of the build platform. A model that lies below the build platform will result in an error and will not print correctly, and a model that lies above the platform will print with severe warping, since the first layer of plastic will have nothing on which to adhere. |
| − | + | ==Converting to gcode, and Print Settings'== | |
Once the model appears in the preview the way it is intended to be printed, it can be converted to gcode by either clicking on the icon at the top of the screen with an arrow and a sheet of paper with a 'g' on it, or clicking on the button on the column to the right labeled "generate gcode." A new window will pop up with settings for how the model is to be printed. | Once the model appears in the preview the way it is intended to be printed, it can be converted to gcode by either clicking on the icon at the top of the screen with an arrow and a sheet of paper with a 'g' on it, or clicking on the button on the column to the right labeled "generate gcode." A new window will pop up with settings for how the model is to be printed. | ||
| − | Slicing Profile: It is best to use Replicator Slicing Defaults, since the machine being used is a Replicator | + | * Slicing Profile: It is best to use Replicator Slicing Defaults, since the machine being used is a Replicator. |
| + | |||
| + | * Extruder: Since the Replicator has a dual extrusion system, either the left or the right extruder can be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Raft/Support: Depending on the shape and orientation of the model, a raft and/or supports might be necessary to print. Objects with flat bottoms and no overhangs do not require a raft or supports. A raft should be used for objects with a rounded, curved, or otherwise nonuniform bottom, or for an object with relatively little surface area on the bottom. The raft will add a stable, flat bed of plastic on which the printed object can adhere. If the object has overhangs, or very steep vertical curves, supports will be needed in addition to the raft. Supports are essentially pillars of plastic printed under the overhangs or curves so that the overhangs have something to rest on as they are being printed. The supports and rafts can be cut away from the final product after it has finished printing. | ||
| − | + | ==Printing and General Maintenance== | |
| + | * Do not set the extruder temperature too high or it will reduce the coefficient of friction on the filament and the stepstruder to a point where it cannot extrude anymore. | ||
| + | * Makerbot people recommend cleaning the printer after about 50 hours of printing or so | ||
| + | * If your model has trouble sticking: | ||
| + | **Clean the plate. | ||
| + | **Make ABS goop and paint a thin layer on, this will help the filament stick to the plate more easily. | ||
| − | + | === '''Overhang / Supports''' === | |
| − | + | Software: Meshmixer | |
| + | |||
| + | Once you import a pre-existing model: | ||
| + | * If model is not on bed: | ||
| + | ** Under the "Edit" tab, click "Align" | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Under the "Analysis" tab, click "Overhang" | ||
| + | ** The "Support Generator" tab can be used to change the settings of the supports | ||
| + | *** Base and Post diameters are the only options that need to be changed | ||
| + | *** The taller the model, the larger the posts should be | ||
| + | *** If the supports have trouble sticking to the bed, make the base diameter bigger | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Press "Generate Supports" when ready | ||
| + | * Use the "Delete Supports" button to delete supports before trying to apply any changes to the support settings | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Use the "Export" tab on the bottom left to export as " *.stl " when finished | ||
| + | ==3D Modeling== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Post-Processing== | ||
| + | Turn off the printer and take your print off the plate | ||
| + | |||
| + | Removing the model off the bed | ||
| + | *Wait for the plate to cool completely | ||
| + | *Gently use the plastic spatula or flat head screw driver, to lift a corner of the model off of the bed | ||
| + | **Do not scrape or scratch at the model, the bed will be damaged | ||
| + | *Once a corner of the model has been lifted, use the spatula to slowly lift the rest of the model off of the bed | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fixing the model | ||
| + | *If there are tears in the model that might compromise the integrity of the model, use acetone to weld the model back together | ||
| + | *Ask the Chemistry Department for acetone | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Pricing= | ||
| + | Cost of each print will be determined by its weight | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cost = ( print weight / 1 Kg ) x price of spool x 2* | ||
| + | |||
| + | TAZ Spool Price: $80 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Robo3D Spool Price: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example TAZ Prints: | ||
| + | {|style="margin: 0 auto;" | ||
| + | |[[File:Large_Cup.jpg|thumb|300px|A large cup: $18.18 ~11 hour print 113.68g]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Sail_Boat.jpg|thumb|300px|A small sailboat: $1.59 ~1 hour print 9.95g]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Pen_Stand.jpg|thumb|300px|A pen stand: $2.18 ~1.5 hour print 13.63g]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Phone_Stand.jpg|thumb|300px|A simple phone stand: $2.67 ~2.2 hour print 16.66g]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {|style="margin: 0 auto;" | ||
| + | \[[File:Microscope_Phone_Adapter.jpg|thumb|300px|An adapter to hold a phone over the microscope: $11.44 ~5.9 hour print 71.52g]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>There is currently a 100% up-charge to maintain the printers and purchase more filament | |
Latest revision as of 15:36, 27 October 2020
Following is a detailed description of how to use the 3D printers located in Babbage. Currently, the Lulzbot Taz 5 is the only printer in working order. The process starts with a design in an STL file format. The computers in Babbage are equipped with OpenSCAD software, as well as Fusion 360. however, any design software can be used as long as the file is exported in an .stl format. For the Lulzbot Taz 5, Cura is used to preparing the design for printing and control the printer. The actual printing takes a long time and requires a lot of patience especially when ensuring a good first layer. Sit down to print with a mind open to repeated failure, only then will you be able to achieve a successful print worthy of your time and the resources used.
Contents
- 1 Introducing our 3D printers:
- 2 Printing instructions:
- 3 Introduction Pegasus Touch Laser SLA 3D Printer
- 4 Introduction MakerBot Replicator
- 5 Pricing
Introducing our 3D printers:
Printing instructions:
Instructions on how to use the 3D printers:
Lulzbot Taz 5
Software for the printer: Cura
Steps for printing:
- turn on the printer using the power switch on the Lulzbot
- open Cura, click on the "monitor" tab and click "connect" located about halfway down the sidebar in the controls section
- once the printer is connected preheat the nozzle and the bed by clicking "preheat" the nozzle will automatically preheat to 245deg C, the bed has a default of 75deg C but should be set to preheat at 90deg C
- while the printer is preheating go to the "prepare tab" and open your design file
- scale and position the design making sure it will print in a stable position (usually it will do this automatically)
- If there are any dramatic overhangs in the design, click the "generate support" box, Cura will generate supports for those parts of the model which are thin enough that they can be removed after the design is printed
- selecting a base type is subjective based on the model, if it is unbalanced it may need it. It is recommended to at least use the "skirt" base option, this prints a circle around the model. This is helpful because often the extruder does not function perfectly when it first starts printing due to the polymer building up in the nozzle
- once you have prepared the design click on the monitor tab and click "start print" at the bottom of the sidebar
- adjust the knob on the printer to lower the print speed to 50% to ensure a good first layer
- you may have to use the tweezers to pull off melted filament from the nozzle if it starts to build up as the printer is running through its preperation steps before it starts printing the design
- watch to ensure a solid first layer then the knob on the printer can be adjusted to 100% speed
- once the printer has completed a few layers and you are content with the initial results you should be able to sit back and let the printer work its magic
- the printer can be left unattended while printing but should be checked on periodically
- let the bed cool to around 50deg before removing the print
troubleshooting the first layer
The first layer is important to ensure a good final print and to make sure the printer is functioning correctly. If there are minor issues with the first layer you can keep watching and see if the subsequent layers cover up the errors sufficiently. However, if there are major problems you should abort the print, scrape off what was printed on the build plate with the plastic spatula, and start over. The build plate and nozzle will have to reheat again but they should still be close to the desired temperature.
If the filament is not extruding properly
- abort the print
- go to the controls section and rise the extruder a little bit off the build plate by clicking the up arrow for the z-axis several times
- using the tweezers pull off any built-up filament form the tip of the extruder
- next, click "extrude" 5-15 times until the filament is flowing correctly from the nozzle/extruder (note: it is a little delayed so filament will not immediately come out right when you click extrude"
- remove the printed material from the build plate
- start the print again
If the filament is extruding properly but not adhering to the build plate
- abort the print
- remove the printed material from the build plate
- if a glue stick is available, apply to the area of the build plate where the design will be printed
- alternatively, you could try wiping the build plate down with a paper towel with some alcohol on it (there should be some isopropyl alcohol on the shelves above the Lulzbot)
- start the print again
Robo R1+ 3D Printer
Software for the printer: MatterControl
Printing from an SD card:
- Insert a microSD card into the Mac and get rid of any files in it.
- Open MatterControl and drag your .stl file into the QUEUE section of the application.
- On the top-left section, click on “Select Printer.” Select “Robo 3D TM Turing” in the window that pops out.
- Towards the bottom of the QUEUE section, you will find a “Queue” button. Click on it to get a list.
- On the list, below GCode, select “Export to Folder or SD Card.” Click on the microSD card under “Devices” in the side panel and click on “Export”
- Now, in Finder, browse to the microSD card and rename the file you just exported as “auto0.g” (auto zero dot g). Choose “Use.g” if a prompt appears.
- Then, safely remove the microSD card from the Mac and insert it into the Robo 3D printer.
- Prep the build plate using one the following:
- Glue Stick
- Vinyl Sheeting
- Hairspray
- Apply whichever product on the surface of the build plate enough to cover the surface you will be printing on.
- Turn the printer on. Your print will start after about 5 minutes.
- After the print is over, wait for the temperature to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object from the build plate.
- Clean the build plate.
Printing from the computer:
- Open MatterControl and drag your .stl file into the QUEUE section of the application.
- On the top-left section, click on “Select Printer.” Select “Robo 3D TM Turing” in the window that pops out.
- Under "Settings" ensure that the correct material is selected.
- Under "Controls" an offset of 0.9 typically shows the best results.
- Pre-heat the extruder and bed on the same page.
- Alternatively, near the top center of the screen, an extruder temperature and a bed temperature will be shown, mouse over and click "pre-heat" for both.
- Prep the build plate using one the following:
- Glue Stick
- Vinyl Sheeting
- Hairspray
- Click print once the printer has heated up.
- After the print is over, wait for the temperature to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object from the build plate.
- Clean the build plate.
MakerBot 3D Printer
Software for the printer: ReplicatorG
Steps to follow in order to print:
- Insert a microSD card into the Mac.
- Open ReplicatorG, drag and drop your stl file into application screen.
- Adjust your model if you need to.
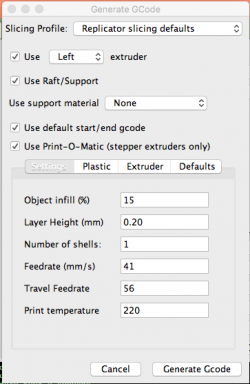
- Select “Generate GCode” on the bottom right.
- Make sure the values are set as shown in the image below and then select “Generate GCode”
- If prompted with an “Acceleration Warning” select “OK”
- Wait until it generates the gcode.
- After the file is generated go to the gcode tab and modify the numbers on the lines M104 should be 230 and M109 should be 128, i.e.:
- M104 S230 T1 (set extruder temperature) M109 S128 T1 (set HBP temperature)
- Make sure to save it by pressing “Command + S”.
- Select “Build to file using SD Card” as shown in the image below. Select the microSD card and make sure to save it as “.x3g” format.
- Wait until it is done building and then safely eject the sdCard from the Mac and insert it into the MakerBot. Note: You can find the sdCard slot as shown in the image below:
- Turn on the printer.
- Select “Build from SD” and then using the arrows scroll down to your file.
- The printer will start heating up and once it finishes heating up, it will start printing.
- Once the printing has finished, wait for the bed to cool down and carefully remove the 3D printed object.
Introduction Pegasus Touch Laser SLA 3D Printer
The SLA printer currently being used in the display case in Dennis is a Pegasus Touch by FSL3D. The Pegasus Touch prints with a clear Photopolymer resin, and has a build volume of 7”x7”x9” (177x177x228mm).
FSL3D Resources
See below for a number of helpful resources for operating the Pegasus Touch provided by FSL3D:
Pegasus Touch product page and full system specs
FSL3D Wiki space and Pegasus Touch user manual
FSL3D Software and manual downloads
Safety
There are a number of safety hazards involved in the operation of the Pegasus Touch. Please exercise caution and take note of the guidelines below.
Work Area
The printer must be installed on a level surface in order to prevent resin spillage. It should also be kept away from direct sunlight, as this can interfere with the printing process and effect the resin being used. Although the printer does not emit any fumes, a well-ventilated area should be identified for using isopropyl alcohol to finish printed parts.
Photopolymer Resin
The Photopolymer resin is irritating to the eyes, respiratory system and skin. Direct contact with the liquid resin should be minimized, and exposed skin should be washed thoroughly after handling. It is advisable to use impermeable, chemical-resistant gloves when handling the resin, and safety goggles or glasses if possible. Resin containers should remain sealed, and the opening of the Pegasus Touch should be kept to a minimum while there is resin in the build area. In addition, resin should not be allowed to drip into the Pegasus Touch outside of the build area.
Before handling the resin, see:
Laser Safety
The printer should remain CLOSED while operating. The autolock should only be overridden in the case of an emergency, and only with proper eye protection. Opening the printer during a job, without pausing it, can expose you to class 3B laser radiation.
Setup
- Ensure that the machine is properly connected:
- The ethernet port on the machine connects to the nearby freeport on the wall.
- The power adapter plugs into the nearby power outlet on the wall.
- The DC barrel connector plugs into the power port on the machine.
- If turned off, the machine should boot within 90 seconds of being properly connected.
- Ensure that the build head and resin vat are securely fastened and leveled. If the build head and vat are not securely fastened and leveled, refer to the discussion of the procedure in the maintenance section.
- Ensure that the build head has been properly cleared of all resin remaining from previous prints. If resin remains on the build head, refer to the discussion of cleaning the build head in the post-production section.
- Ensure that you have access to isopropyl alcohol (or a similar alcohol), a safe container to use, and chemical-resistant gloves for the finish process
- Fill the vat with resin up to the minimum fill line, or the first step.
Printing
To print from the Pegasus Touch, first download FSL3D's RetinaCreate software and ensure a secure internet connection:
Download RetinaCreate Software Windows Vista – 8.1
Download RetinaCreate Software Mac OS X 10.9 *ALPHA PREVIEW*
NOTE: The OS X version of the software is EXTREMELY minimal. Thus far we have not had success in using it to print on the Pegasus Touch. Therefore is is highly recommended that you use RetinaCreate for Windows. This has not been done successfully yet, and the only prints created with the Pegasus Touch have been test prints that come pre-loaded on the device. If you experiment with the Windows version of the software, please document your experience here. A good guide can be found here.
Resin
If needed, more resin may be added the vat during a print. To do this, make sure that you pause the print using the LCD interface before opening the printer to add more resin. Do not add resin up to the maximum fill line until at least 10cm of printing has been completed, so that it does not overflow.
Post-Production
- When the model has finished, wait at least 10 minutes to allow excess resin to drip into the vat before opening the lid.
- It is recommended that you insert a cutting board or other safe surface on top of the vat before removing the build head. This is to prevent excess resin from dripping into the machine.
- Remove the build platform by unscrewing the fastening bolt, gently sliding it out, and flipping it over once it is out of the printer.
- Scrape any excess resin back into the vat before taking the model to an acceptable finish station.
Note: finished parts may remain on the build platform form up to several days as long as the lid is left shut and the printer is kept out of direct contact with UV sunlight.
Finishing steps
- Scrape or pull the model(s) off of the build platform (ensure that you are using gloves to prevent direct skin exposure to the resin).
- Place the model(s) into a safe container and submerge them in isopropyl alcohol or a similar alcohol for 15 minutes.
- Remove the model(s) from the alcohol and carefully remove the support structure.
- Rub the build platform with IPA, rinse and dry before replacing it.
- If there is still resin in the printer's vat, make SURE that the lid of the Pegasus Touch remains closed after you are done.
Maintenance
A number of maintenance procedures must be periodically performed to ensure that the Pegasus Touch continues to move smoothly.
Build plate leveling
The build plate should be re-leveled if the build plate and the bottom of the vat are not properly aligned, or if the Pegasus Touch is ever physically moved. A video tutorial that outlines this process may be found here:
Motor calibration
The motor may be manually calibrated if necessary. This will reset the starting z-position of future prints, and should be done if the Pegasus Touch is moved or exposed to significant temperature changes. To manually calibrate the motor, navigate the LCD display to the motor calibration screen and lower the build plate using the ‘Motor Down’ button until it nearly touches the vat. Then, finely adjust the build plate level by opening the case and twisting the lead screw manually. The goal is to leave less than 0.5mm of space between the build plate and the vat. Once this is accomplished, press the ‘Set Motor Homing’ button. The motor will then raise the build plate a few centimeters automatically. Verify that the homing has been set accurately by pressing the ‘Test Motor Homing’ button and seeing that the build plate returns to the position hovering slightly above the vat.
Laser calibration
We have yet to perform laser calibration. Please update this page with your experiences if you calibrate the laser.
Introduction MakerBot Replicator
The printer currently being used in the physics lab Dennis 128 is a MakerBot Replicator. The Replicator can print both ABS and PLA filament, and has a build volume of 8.9" L x 5.7" W x 5.9" H. ((255x145x150mm) It also comes equipped with a dual extrusion system to be able to print objects in two colors.
Makerbot Replicator product page and full system specs
Software
A very user-friendly program to use to communicate with the Replicator is MakerBot's own ReplicatorG, which can be found as a free download here: http://replicat.org/download. There are installation instructions included on that website, as additional downloads are required (Python and some drivers).
Desiging your own 3D model:
Cheat Sheet: http://www.openscad.org/cheatsheet/index.html
After creating your own 3D model follow these steps:
- Render and compile your code by pressing F6
- Export the design as .stl
- If the file is in your own computer, move the file(name.stl) to the Mac found in Turing lab(CST 222)
All programs mentioned are free.
OpenSCAD
Open source. Programmatic 3d modeling. Very precise, units in millimeters.
Preparing a model in OpenSCAD for printing
- You’ll need:
After creating your own 3D model follow these steps:
- Render and compile your code by pressing F6
- Export the design as .stl
- If the file is in your own computer, move the file(name.stl) to the Mac found in Turing lab(CST 222)
For the pegasus printer
- open that stl in ReplicatorG
- center the object and put on platform if necessary
generate gcode
- recommended settings: left extruder, 15% infil, .20 layer height, 35 extruder and motor speed
- Wait.
- After the file is generated go to the gcode tab and modify the numbers on the lines M104 should be 230 and M109 should be 128, i.e.:
M104 S230 T1 (set extruder temperature)
M109 S128 T1 (set HBP temperature)
- export file to disk
Blender
Open source. The best open source modeler out there, very powerful, hard to get to be precise for engineering centric designs. After exporting a model to an .stl you'll want to run the model through Netfabb which will check to make sure the model has no holes or connected meshes that share a single edge.
Google SketchUp
Maintained by Google, tutorials available.
Thingiverse
3D models can be uploaded and downloaded online through a free website called Thingiverse.
ReplicatorG
ReplicatorG is the main interface between the 3D model and the printer. Since 3D models are usually .cad, .obj, or .stl files, the printer cannot directly print them. ReplicatorG uses a tool called Skeinforge to take the 3D model as a .stl file, and turn it into gcode. Skeinforge slices the model into layers and determines what paths the extruder needs to take for each layer based on the parameters set in ReplicatorG. The resulting file is a .gcode file, which can be printed directly from the computer if connected via USB. To print without connecting a computer, the .gcode file needs to be converted to a .s3g file and saved to an SD card, as discussed below.
Interface
ReplicatorG will display a 3D interactive preview of the open .stl file. The column on the right offers some options on how to orient the model on the actual build platform. Some of these options include moving, rotating, or scaling the model before it is printed. It has default "snap-to" settings to center the model on the platform, and move it so that its bottom-most side (the first layer) is laying just on the surface of the build platform. A model that lies below the build platform will result in an error and will not print correctly, and a model that lies above the platform will print with severe warping, since the first layer of plastic will have nothing on which to adhere.
Converting to gcode, and Print Settings'
Once the model appears in the preview the way it is intended to be printed, it can be converted to gcode by either clicking on the icon at the top of the screen with an arrow and a sheet of paper with a 'g' on it, or clicking on the button on the column to the right labeled "generate gcode." A new window will pop up with settings for how the model is to be printed.
- Slicing Profile: It is best to use Replicator Slicing Defaults, since the machine being used is a Replicator.
- Extruder: Since the Replicator has a dual extrusion system, either the left or the right extruder can be used.
- Raft/Support: Depending on the shape and orientation of the model, a raft and/or supports might be necessary to print. Objects with flat bottoms and no overhangs do not require a raft or supports. A raft should be used for objects with a rounded, curved, or otherwise nonuniform bottom, or for an object with relatively little surface area on the bottom. The raft will add a stable, flat bed of plastic on which the printed object can adhere. If the object has overhangs, or very steep vertical curves, supports will be needed in addition to the raft. Supports are essentially pillars of plastic printed under the overhangs or curves so that the overhangs have something to rest on as they are being printed. The supports and rafts can be cut away from the final product after it has finished printing.
Printing and General Maintenance
- Do not set the extruder temperature too high or it will reduce the coefficient of friction on the filament and the stepstruder to a point where it cannot extrude anymore.
- Makerbot people recommend cleaning the printer after about 50 hours of printing or so
- If your model has trouble sticking:
- Clean the plate.
- Make ABS goop and paint a thin layer on, this will help the filament stick to the plate more easily.
Overhang / Supports
Software: Meshmixer
Once you import a pre-existing model:
- If model is not on bed:
- Under the "Edit" tab, click "Align"
- Under the "Analysis" tab, click "Overhang"
- The "Support Generator" tab can be used to change the settings of the supports
- Base and Post diameters are the only options that need to be changed
- The taller the model, the larger the posts should be
- If the supports have trouble sticking to the bed, make the base diameter bigger
- The "Support Generator" tab can be used to change the settings of the supports
- Press "Generate Supports" when ready
- Use the "Delete Supports" button to delete supports before trying to apply any changes to the support settings
- Use the "Export" tab on the bottom left to export as " *.stl " when finished
3D Modeling
Post-Processing
Turn off the printer and take your print off the plate
Removing the model off the bed
- Wait for the plate to cool completely
- Gently use the plastic spatula or flat head screw driver, to lift a corner of the model off of the bed
- Do not scrape or scratch at the model, the bed will be damaged
- Once a corner of the model has been lifted, use the spatula to slowly lift the rest of the model off of the bed
Fixing the model
- If there are tears in the model that might compromise the integrity of the model, use acetone to weld the model back together
- Ask the Chemistry Department for acetone
Pricing
Cost of each print will be determined by its weight
Cost = ( print weight / 1 Kg ) x price of spool x 2*
TAZ Spool Price: $80
Robo3D Spool Price:
Example TAZ Prints:
*There is currently a 100% up-charge to maintain the printers and purchase more filament